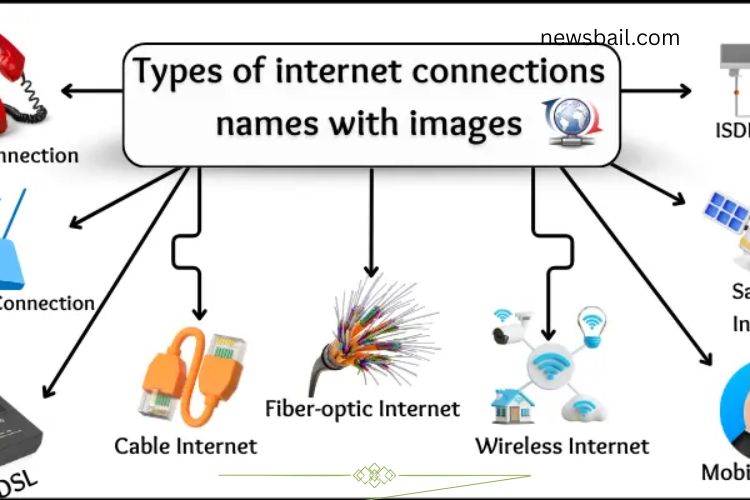
Internet connectivity powers communication, business, education, and entertainment across the globe. Different types of internet connections use distinct technologies to deliver online access, and each option offers unique advantages in terms of speed, reliability, and availability. Understanding these internet connection types helps users choose the best solution for their homes, offices, or remote locations.
Dial-Up Internet Connection
Dial-up internet represents one of the earliest forms of online connectivity. This traditional internet connection uses a telephone line and a modem to establish access. The modem dials a specific number through the phone network, creating a temporary connection to the internet.
Speed remains extremely limited with dial-up, typically reaching up to 56 kbps. Users cannot make phone calls while browsing because the same line handles both services. Web pages load slowly, and streaming or large downloads become nearly impossible.
Despite these limitations, dial-up internet played a crucial role in introducing millions of people to the digital world. Today, it has largely disappeared due to faster and more efficient broadband technologies.
Broadband Internet Connection
Broadband internet transformed online access by delivering significantly higher speeds than dial-up. Unlike older systems, broadband allows users to access the internet and use their telephone simultaneously. This always-on connection eliminates the need to dial in each time.
Broadband internet supports faster browsing, smoother video streaming, and efficient file downloads. Homes and offices widely adopt broadband because it improves productivity and enhances online experiences. Various technologies, including DSL, cable, and fiber, fall under the broadband category.
Reliable performance and consistent connectivity make broadband one of the most popular internet solutions worldwide.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
DSL, or Digital Subscriber Line, uses existing telephone lines to deliver digital internet signals. Unlike dial-up, DSL transmits data digitally rather than converting it into sound signals. This technology ensures faster and more stable internet performance.
Users can browse the web and talk on the phone at the same time without interruption. DSL speeds vary depending on distance from the service provider, but it generally performs better than dial-up.
Many households and small businesses prefer DSL internet because it offers affordable pricing, simple installation, and dependable speeds for everyday online tasks such as email, browsing, and streaming.
Cable Internet
Cable internet uses the same coaxial cables that deliver television services. A cable modem connects the network line to a computer or Wi-Fi router, providing high-speed internet access.
Compared to DSL, cable internet typically offers faster download speeds. It handles streaming, online gaming, and large downloads efficiently. Urban and suburban areas widely use cable internet due to its strong performance and broad availability.
However, cable internet shares bandwidth among users in the same neighborhood. During peak hours, speeds may slow slightly if many people connect simultaneously. Even so, cable remains a powerful and reliable internet option for most households.
Fiber-Optic Internet
Fiber-optic internet delivers the fastest internet speeds available today. This advanced technology uses thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as light signals instead of electrical signals. As a result, fiber internet achieves extremely high speeds and low latency.
Fiber connections support heavy data usage, including 4K streaming, video conferencing, cloud computing, and competitive online gaming. Businesses rely on fiber-optic internet for secure and stable communication.
Exceptional reliability and ultra-fast performance position fiber-optic internet as the future of high-speed connectivity. Availability continues to expand, especially in major cities and developed regions.
Wireless Internet (Wi-Fi)
Wireless internet, commonly known as Wi-Fi, allows devices to connect without physical cables. A wireless router transmits internet signals through radio waves, enabling smartphones, laptops, tablets, and smart devices to access the network.
Wi-Fi enhances convenience by supporting multiple devices simultaneously. Homes, offices, schools, and public spaces rely on wireless internet for seamless connectivity.
Performance depends on router quality, signal strength, and network congestion. Strong security settings, including passwords and encryption, protect wireless networks from unauthorized access. Wi-Fi remains essential for modern digital lifestyles.
Mobile Internet (3G, 4G, 5G)
Mobile internet provides wireless connectivity through cellular networks. Smartphones and other devices use SIM cards to connect to nearby mobile towers.
Third-generation (3G) networks introduced mobile browsing and basic video streaming. Fourth-generation (4G) significantly improved speed and reliability, supporting HD streaming, social media, and online gaming. Fifth-generation (5G) now delivers ultra-fast speeds, minimal latency, and the ability to connect numerous smart devices simultaneously.
Mobile internet offers unmatched flexibility because users can access the web almost anywhere within network coverage. Continuous advancements in cellular technology drive faster performance and smarter connectivity worldwide.
Satellite Internet
Satellite internet connects users through satellites orbiting the Earth. A satellite dish installed outside the home communicates with a satellite, which then links to an internet service provider.
This type of internet proves valuable in rural or remote areas where cable, DSL, or fiber infrastructure does not exist. Satellite internet ensures connectivity in mountains, deserts, and isolated communities.
Weather conditions such as heavy rain or storms may affect signal strength. Although speeds have improved significantly in recent years, latency can remain higher compared to fiber or cable connections. Nevertheless, satellite internet continues to bridge the digital divide in underserved regions.
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network)
ISDN, or Integrated Services Digital Network, represents an early digital internet technology. It used digital telephone lines to transmit voice and data simultaneously. ISDN improved upon dial-up by offering faster speeds and better call quality.
Businesses adopted ISDN for video conferencing and data transfer before broadband became widely available. However, newer technologies such as DSL, cable, and fiber have largely replaced ISDN due to superior speed and efficiency.
Today, ISDN exists mainly in legacy systems, while modern broadband solutions dominate the internet landscape.
Choosing the Right Internet Connection
Selecting the best internet connection depends on location, budget, usage needs, and availability. Fiber-optic internet delivers unmatched speed and reliability for high-demand users. Cable and DSL provide dependable performance for households and small businesses. Mobile and satellite internet offer flexible solutions for travel and remote regions.
Careful evaluation of internet speed, data limits, installation costs, and long-term reliability ensures the right decision. Strong and stable internet connectivity empowers productivity, entertainment, and communication in today’s digital world.
Reliable internet access no longer represents a luxury. It serves as a foundation for education, innovation, and global connection. Understanding different types of internet connections allows individuals and organizations to choose smarter, faster, and more efficient solutions for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the main types of internet connections?
The main types include dial-up, DSL, cable, fiber-optic, wireless (Wi-Fi), mobile (3G, 4G, 5G), satellite, and ISDN. Each type differs in speed, reliability, and accessibility.
Which internet connection is the fastest?
Fiber-optic internet is currently the fastest, offering ultra-high speeds and stable connections, ideal for streaming, gaming, and large data transfers.
What is the most reliable internet connection for homes?
For most households, cable, fiber-optic, or DSL connections are highly reliable. They provide consistent speed and are less affected by weather or signal interference.
Can I use the internet and phone simultaneously?
Yes. DSL, broadband, and fiber-optic connections allow you to use the phone and internet at the same time. Older dial-up connections, however, block the phone line.
How does mobile internet work?
Mobile internet uses SIM cards and cellular towers to transmit data. 3G, 4G, and 5G networks offer varying speeds, with 5G providing the fastest performance and lowest latency.
Is satellite internet suitable for rural areas?
Yes. Satellite internet is designed for remote locations where cable or fiber cannot reach. While speed and latency can be affected by weather, it ensures connectivity in underserved regions.
Which type of internet is best for gaming and streaming?
Fiber-optic internet is ideal due to its high speed and low latency. Cable internet also performs well, but DSL and mobile networks may experience slower speeds during peak usage.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of internet connections is essential in today’s fast-paced digital world. From traditional dial-up and ISDN to modern fiber-optic and 5G networks, each connection type offers unique advantages in speed, reliability, and accessibility. Choosing the right internet connection depends on your location, usage needs, and budget, whether it’s for streaming, gaming, remote work, or staying connected in rural areas.