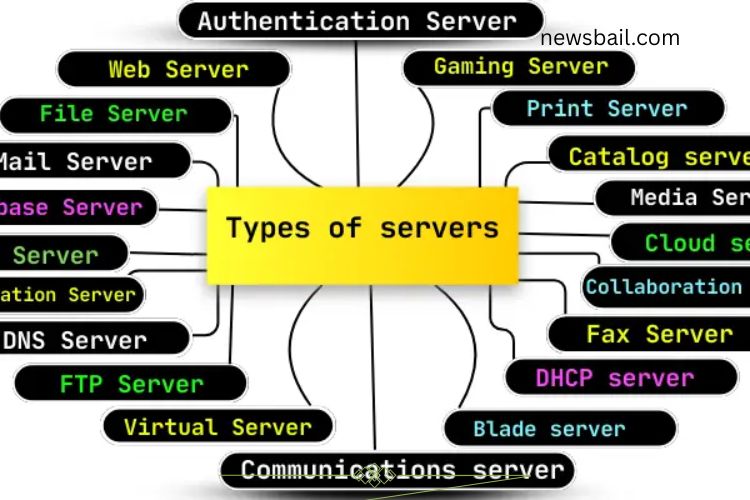
In today’s digital world, servers are the backbone of the internet and networks. Each server type serves a unique purpose, from hosting websites to storing files and managing communications. Understanding these servers helps businesses, schools, and individuals optimize their networks and ensure smooth operations.
Read More: Unlocking the Incredible Potential and Life-Changing Uses of Minicomputers
Web Server
A web server stores and delivers websites to users. When you enter a website address, the server sends the web pages to your browser using the HTTP protocol. Web servers operate continuously, ensuring websites are always accessible. Examples include Apache, Nginx, and Microsoft IIS.
File Server
File servers store and share files across a network. Typically located in a central office or data center, they allow users to save, retrieve, and share documents, photos, and videos securely. Businesses and schools often rely on file servers to keep data organized. Popular options include Windows Server, FreeNAS, and TrueNAS.
Mail Server
Mail servers manage the sending and receiving of emails. They store messages and ensure they reach the intended recipient safely. When you send an email, the mail server routes it to the receiver’s server. Common examples are Microsoft Exchange, Postfix, and Gmail’s servers.
Database Server
Database servers store and manage large volumes of data. They enable users to save, search, and retrieve information efficiently, making them essential for businesses managing customer records, sales data, or inventory. Examples include MySQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server.
Proxy Server
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. It masks your IP address, improves privacy, blocks harmful sites, and can speed up browsing by caching content. Examples include Squid, HAProxy, and Apache Traffic Server.
Application Server
Application servers deliver software and services to users. They support programs like business tools or online shopping apps, processing data and requests to ensure smooth operation. Common examples are Apache Tomcat, WildFly, and WebLogic Server.
DNS Server
DNS servers translate website names into IP addresses, allowing browsers to locate and connect to sites quickly. This process ensures faster, seamless internet browsing. Popular DNS servers include Google DNS, Cloudflare, and OpenDNS.
FTP Server
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) servers enable file uploads and downloads between computers and servers. They are ideal for sharing large files like videos or documents securely. Examples include FileZilla, vsftpd, and ProFTPD.
Virtual #Server
A virtual server is a server running within another physical server. Each virtual server operates independently with its own resources, helping save space and reduce costs. VMware, VirtualBox, and Hyper-V are widely used virtual server solutions.
Gami2ng Server
Gaming servers host online multiplayer games. They manage game data and provide a smooth real-time experience for players. Popular gaming servers support games like Minecraft, Fortnite, and Call of Duty.
Print Server
Print servers connect multiple computers to one or more printers. They manage print jobs, directing documents to the correct printer and simplifying network printing. HP Jetdirect and Lexmark Print Server are common examples.
Catalog Server
Catalog servers store and organize product or service information, including prices, descriptions, and images. They allow businesses to update listings and make it easy for users to search products. Online retailers like Amazon and eBay rely on catalog servers.
Media Server
Media servers store and stream media files such as music, videos, and photos. They allow users to access content on multiple devices over the internet or a local network. Examples include Plex, Kodi, and Windows Media Server.
Authentication Server
Authentication servers verify user credentials before granting access to systems. They ensure security by confirming usernames and passwords. Common examples are Windows Server and LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol).
Collaboration Server
Collaboration servers facilitate teamwork by enabling file sharing, messaging, and project management in real time. They keep shared data secure and make remote collaboration seamless. Examples include Google Drive, Microsoft Teams, and Slack.
Fax Server
Fax servers send and receive faxes digitally, eliminating the need for traditional fax machines. They convert faxes into digital files and deliver them to the recipient securely. MyFax and eFax are widely used solutions.
DHCP Server
DHCP servers automatically assign IP addresses to devices connecting to a network. This ensures devices can communicate and access the internet without manual setup. Home routers and corporate networks often include DHCP servers.
Blade Server
Blade servers are compact, modular servers designed to save space. Multiple blade servers can fit into one rack, sharing power and cooling systems while delivering high performance. Examples include IBM BladeCenter and HP BladeSystem.
Communications Server
Communications servers manage digital interactions such as phone calls, video conferencing, and emails. They maintain smooth communication across networks. Popular solutions include Skype and Zoom.
Cloud Server
Cloud servers host data and applications on the internet. They offer flexibility, remote access, and scalability, eliminating the need for physical hardware. Top providers include Google Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure.
How to Choose the Right Server
Selecting the right server is crucial for efficiency, performance, and security. Follow these steps to pick the perfect server:
- Identify Your Needs: Determine whether you need a server for files, websites, emails, or applications.
- Consider Size: Match the server’s capacity to your personal or business requirements.
- Check Performance: Evaluate processor speed, memory, and storage to ensure it meets your demands.
- Prioritize Security: Look for servers with strong firewalls, backups, and authentication features.
- Budget Wisely: Compare options to find the best balance between cost and functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a server, and why is it important?
A server is a specialized computer that stores, manages, and delivers data, applications, or services to other devices over a network. Servers are essential for websites, emails, file sharing, gaming, and business operations. Without servers, online services and networked communication wouldn’t function efficiently.
How many types of servers are there?
There are numerous server types, each with a unique function. The most common include web servers, file servers, mail servers, database servers, proxy servers, virtual servers, and cloud servers. Overall, there are at least 20 major server types used in businesses and personal networks.
What is a web server, and how does it work?
A web server stores and delivers websites to users. When you enter a website address, it sends the pages to your browser using HTTP. Web servers work around the clock to ensure websites are always available. Popular web servers include Apache, Nginx, and Microsoft IIS.
What is the difference between a virtual server and a physical server?
A physical server is a standalone machine with dedicated hardware, while a virtual server runs on a physical server but operates independently with its own resources. Virtual servers save space, reduce costs, and provide flexibility for running multiple applications.
What is a cloud server, and why is it popular?
A cloud server hosts data and applications over the internet instead of physical hardware. Cloud servers offer remote access, scalability, and flexibility, making them ideal for businesses that need reliable and easily expandable infrastructure. Popular providers include AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
Are servers only for businesses?
No. Servers are valuable for individuals as well. Home users can benefit from file servers, media servers, gaming servers, or cloud servers for personal data management, entertainment, and online collaboration.
How does a proxy server protect my privacy?
A proxy server acts as a gateway between your device and the internet. It hides your IP address, blocks malicious sites, and can cache data to improve browsing speed, making your online activity more secure.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of servers is key to optimizing your digital world. From web servers and file servers to cloud and virtual servers, each serves a unique purpose in managing data, applications, and communications. Choosing the right server ensures efficiency, security, and seamless performance for your personal projects or business operations. By evaluating your needs, performance requirements, and budget, you can select the perfect server to support growth, streamline workflow, and enhance online experiences. Investing in the right server today means reliable, fast, and secure access to the tools and information you need—empowering you to unleash the full potential of your network.